Define a Spark UDF using a DuckDB Spatial function
%md 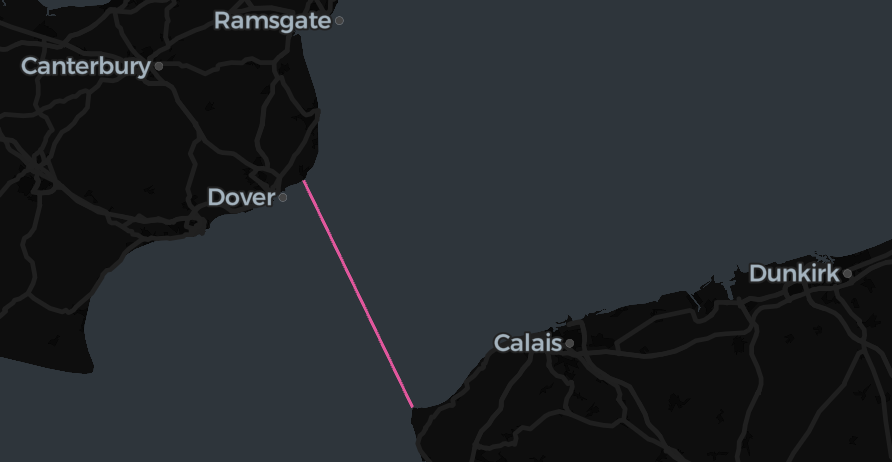
Databricks SQL now contains lots of ST Functions. However, at some point you might just need a geospatial function not (yet) available natively in Databricks, but maybe available in DuckDB Spatial. For example, as of Aug 2025, the st_shortestline function.
Then we can register the DuckDB function as a Spark UDF as follows:
Setup
Define the Spark UDF based on a DuckDB Spatial function
def shortestline_func(a: pd.Series, b: pd.Series) -> pd.Series:
try:
import duckdb
from duckdb import ColumnExpression, FunctionExpression
except ModuleNotFoundError as mfe:
raise Exception(
"'duckdb' not installed: run '%pip install duckdb' first."
) from mfe
duckdb.sql("SET extension_directory = '/tmp/duckdb_ext'")
try:
duckdb.load_extension("spatial")
except duckdb.duckdb.IOException:
duckdb.install_extension("spatial")
duckdb.load_extension("spatial")
df = pd.DataFrame({"a": a, "b": b}) # noqa: F841
res = (
duckdb.df(df)
.select(
FunctionExpression(
"st_aswkb",
FunctionExpression(
"st_shortestline",
FunctionExpression("st_geomfromwkb", ColumnExpression("a")),
FunctionExpression("st_geomfromwkb", ColumnExpression("b")),
),
).alias("res")
)
.df()["res"]
)
return res
st_duckdb_shortestline = F.pandas_udf(shortestline_func, returnType=BinaryType())Usage example
This example uses the CARTO/Overture Maps datasets that you can add to your workspace via the Marketplace.
The CARTO/Overture Maps tables are stored in us-west-2 as of writing, so if you are not using Databricks Free Edition and you are in any other region, you will have to pay egress charges based on the amount of data you read.
%sql
create or replace temporary view lamanche as
with england as (
select
geometry
from
carto_overture_maps_divisions.carto.division_area
where
subtype = 'country'
and country = 'GB'
and class = 'land'
),
france as (
select
geometry
from
carto_overture_maps_divisions.carto.division_area
where
subtype = 'country'
and country = 'FR'
and class = 'land'
)
select
st_duckdb_shortestline(england.geometry, france.geometry) geometry
from
england,
franceNit: To correctly calculate shortestline in the Eucledian sense, we should actually transform lon/lat to an SRID that maintains the angles, such as EPSG:3857. (Then, if we were interested in the length of it in meters, we could transform back to lon/lat and use st_distancespheroid.)
To keep this example simple, we’ll now calculate the shortest line in the lat/lon coordinate system – we will get a quite similar result in this example of Calais-Dover.
Visualizing the result
Let’s visualize the result with Lonboard:
def spark_viz(df, wkb_col="geometry", other_cols=None, limit=10_000, output_html=None):
# needs `%pip install duckdb lonboard shapely`
if other_cols is None:
other_cols = []
from lonboard import viz
try:
duckdb.load_extension("spatial")
except duckdb.duckdb.IOException:
duckdb.install_extension("spatial")
duckdb.load_extension("spatial")
dfa = df.select([wkb_col] + other_cols).limit(limit).toArrow()
if dfa.num_rows == limit:
print(f"Data truncated to limit {limit}")
query = duckdb.sql(
f"""select * replace (st_geomfromwkb({wkb_col}) as {wkb_col})
from dfa
where {wkb_col} is not null"""
)
if output_html is None:
return viz(query).as_html()
else:
viz(query).to_html(output_html)
return output_html